Condition Monitoring Report
Station Number: OH-HM-24
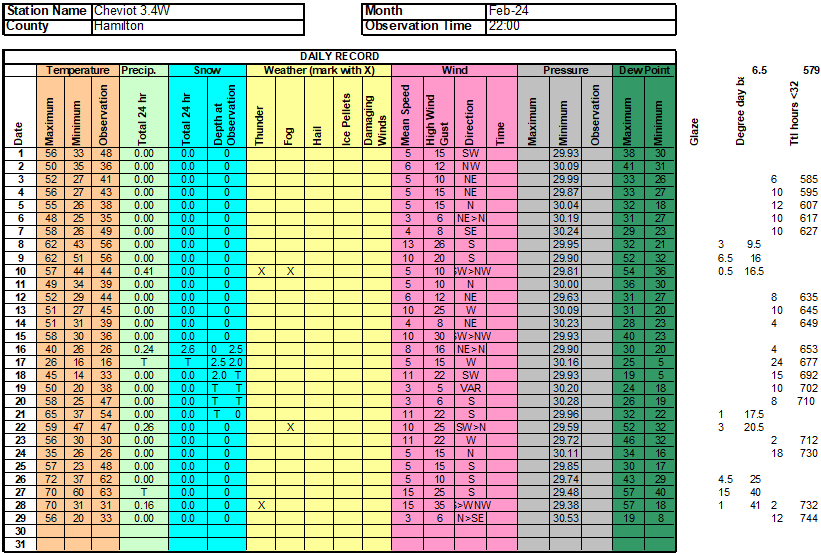
Station Name: Cheviot 3.4 W
Report Date: 2/25/2024
Submitted: 2/25/2024 9:12 PM
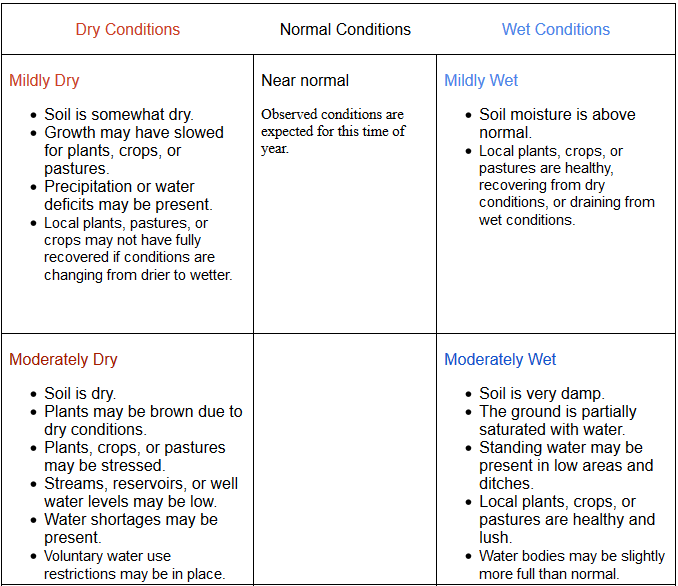
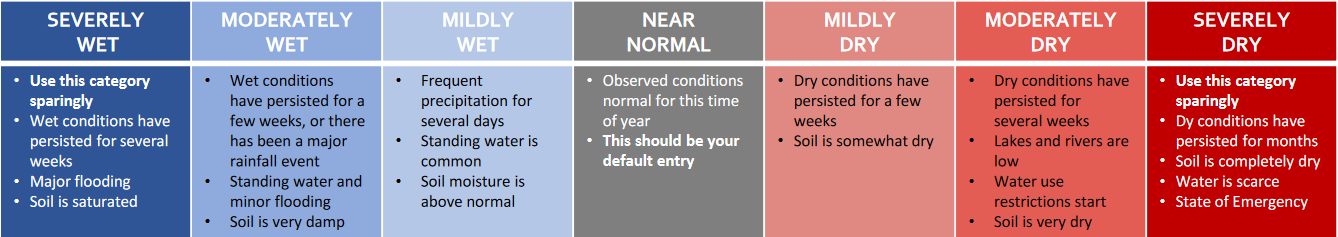
Scale Bar: Mildly Dry
Description:
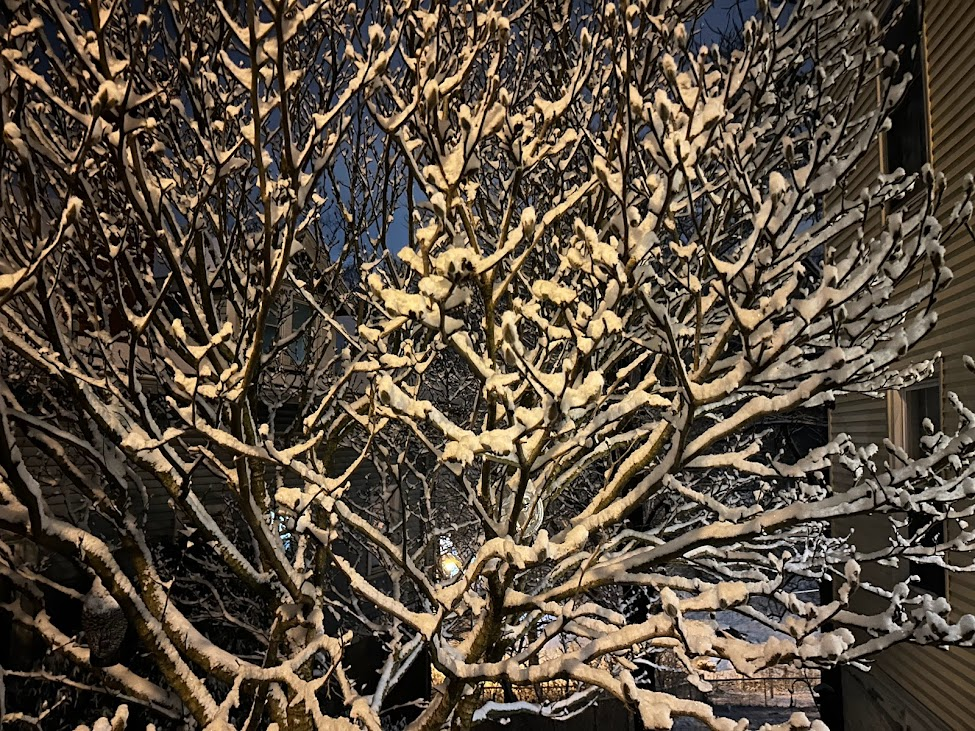
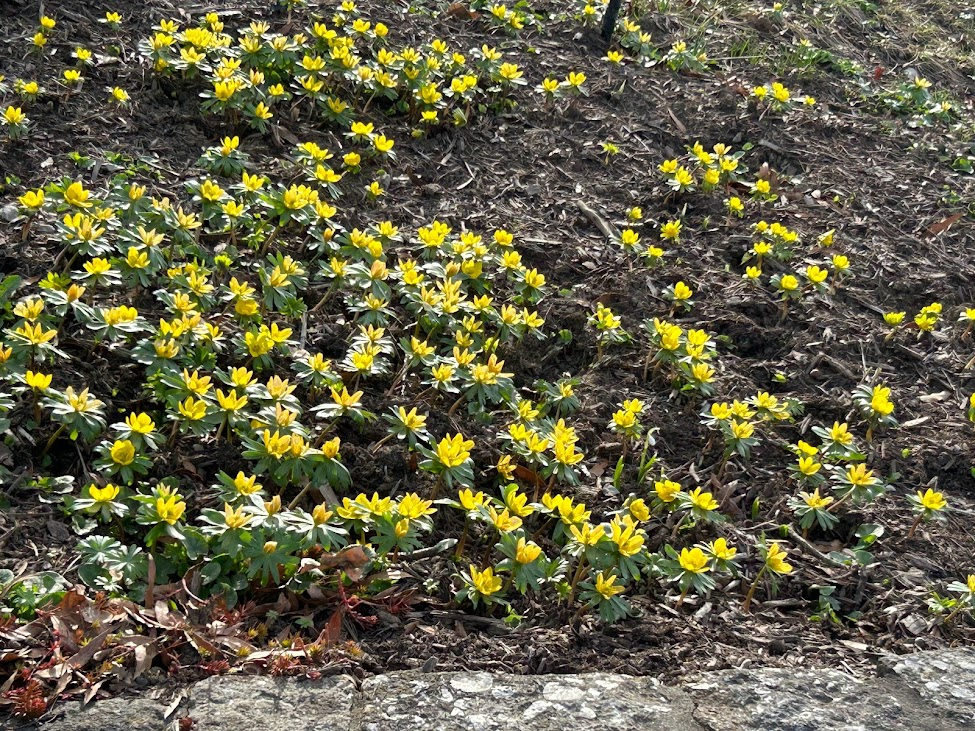
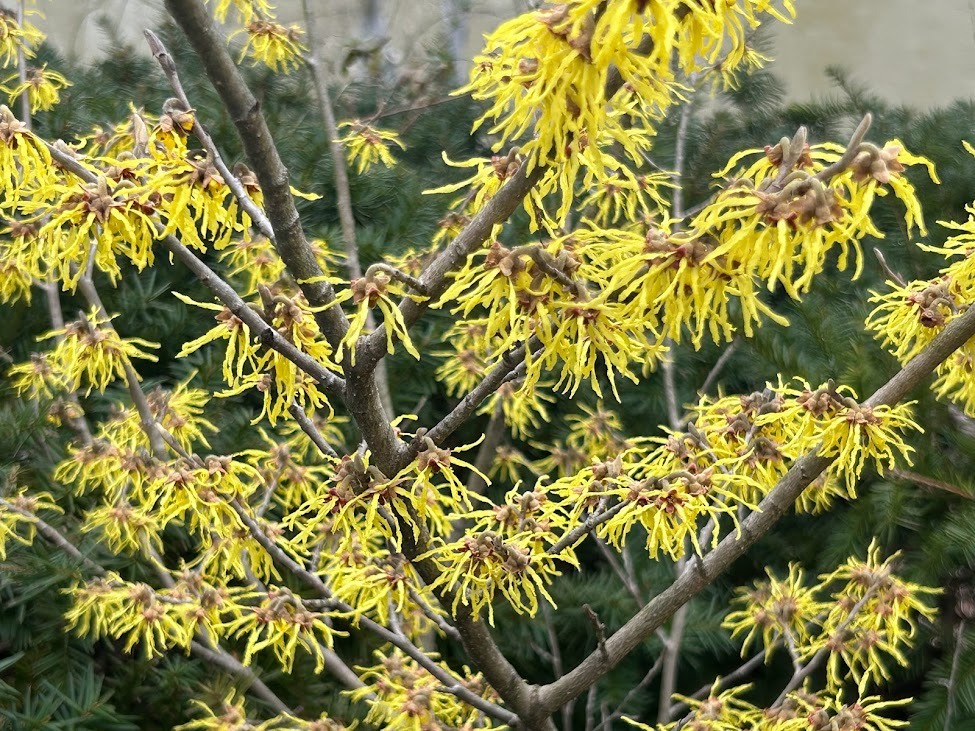
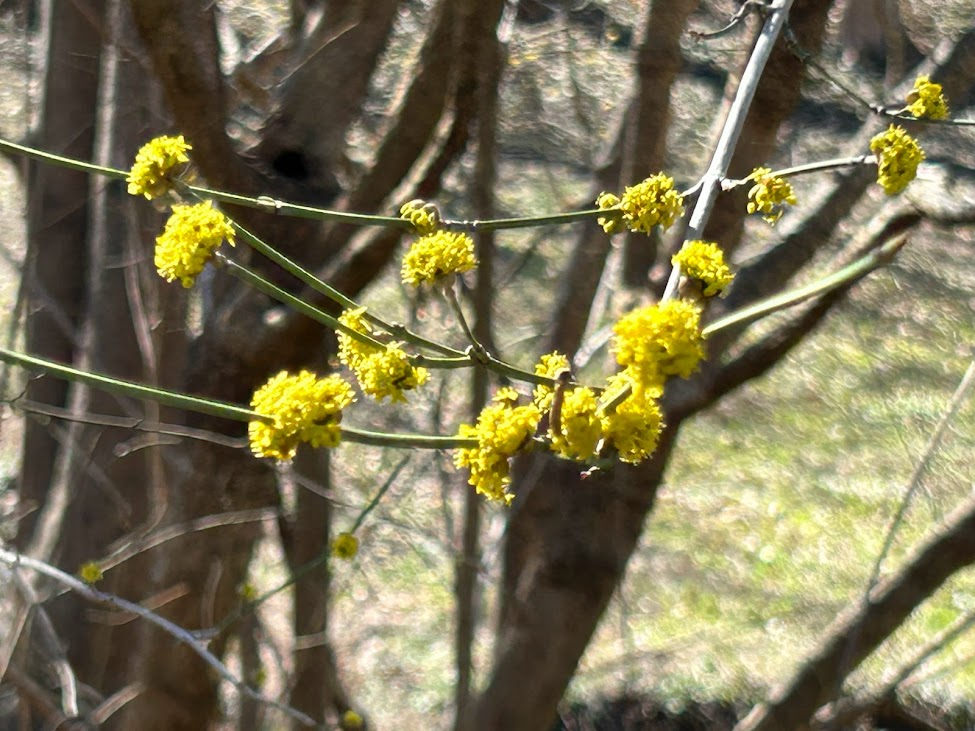
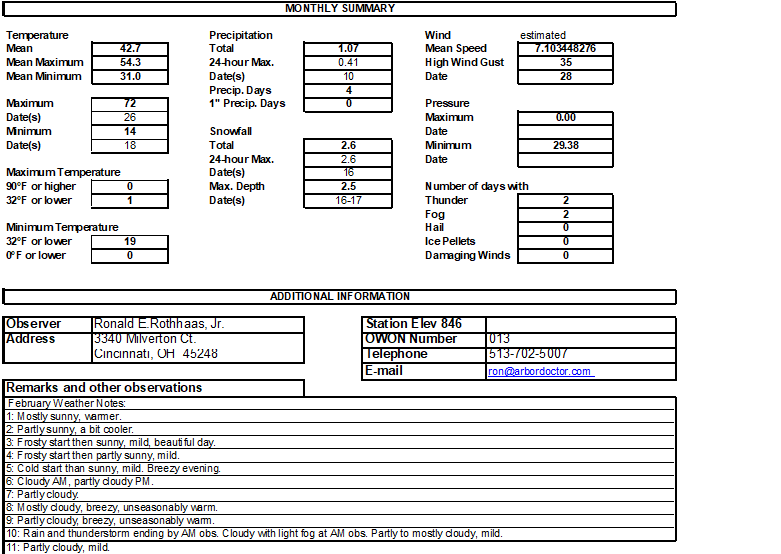
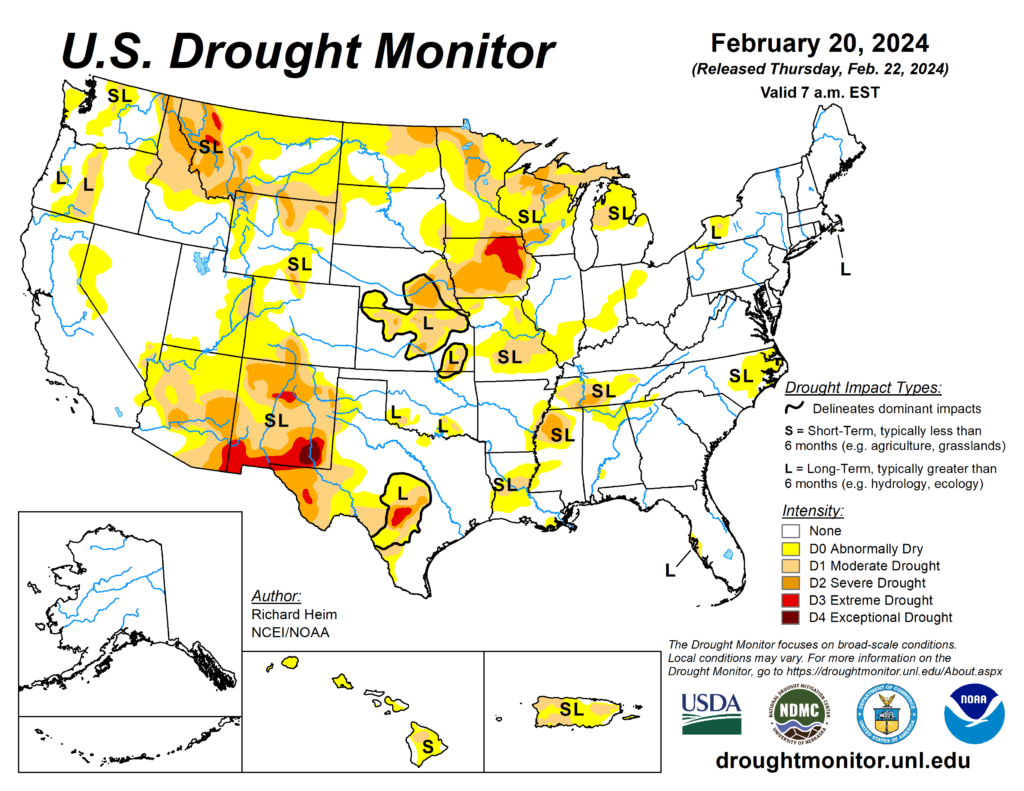
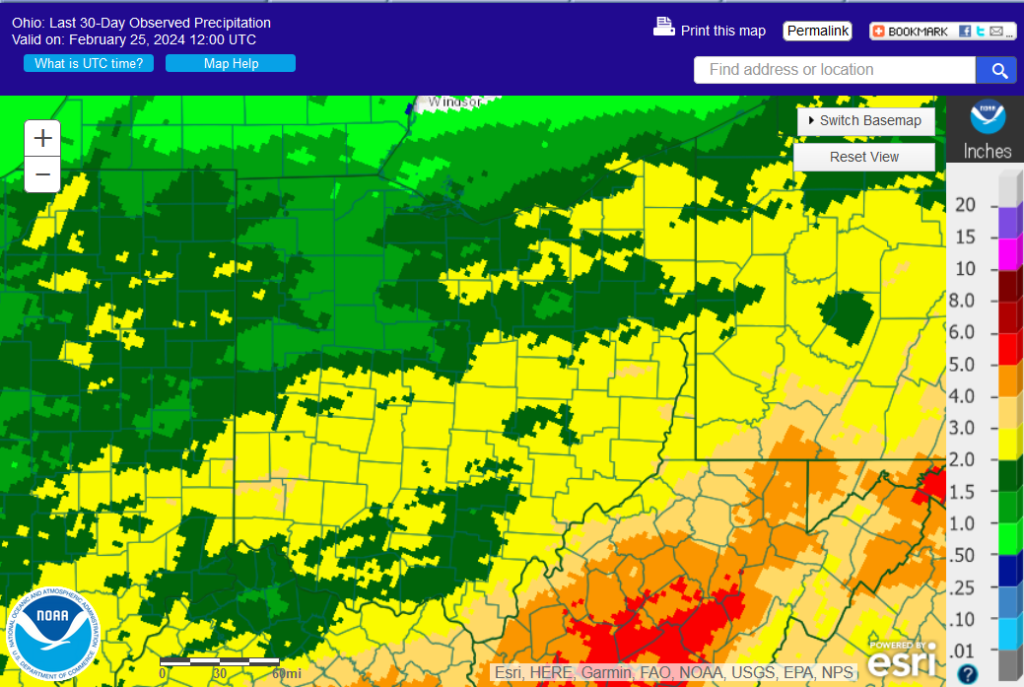
With only 0.91 inches of rain, February’s rainfall is well below average. However, this follows a very wet January so while it has been dry, soil and ground moisture remains good albeit less than what we would expect at this point in the season.
Categories: General Awareness
Agriculture
Plants & Wildlife
Society & Public Health


This report is specifically for the Arbor Doctor’s location 3.4 miles west of Cheviot, OH, in the western suburbs of Cincinnati in southwest Ohio. This location is also an official cooperative observation site for the National Weather Service listed as Cheviot 3W.
What is the Condition Monitoring Report? See these links for more information:
Explanation of scale bar>>>
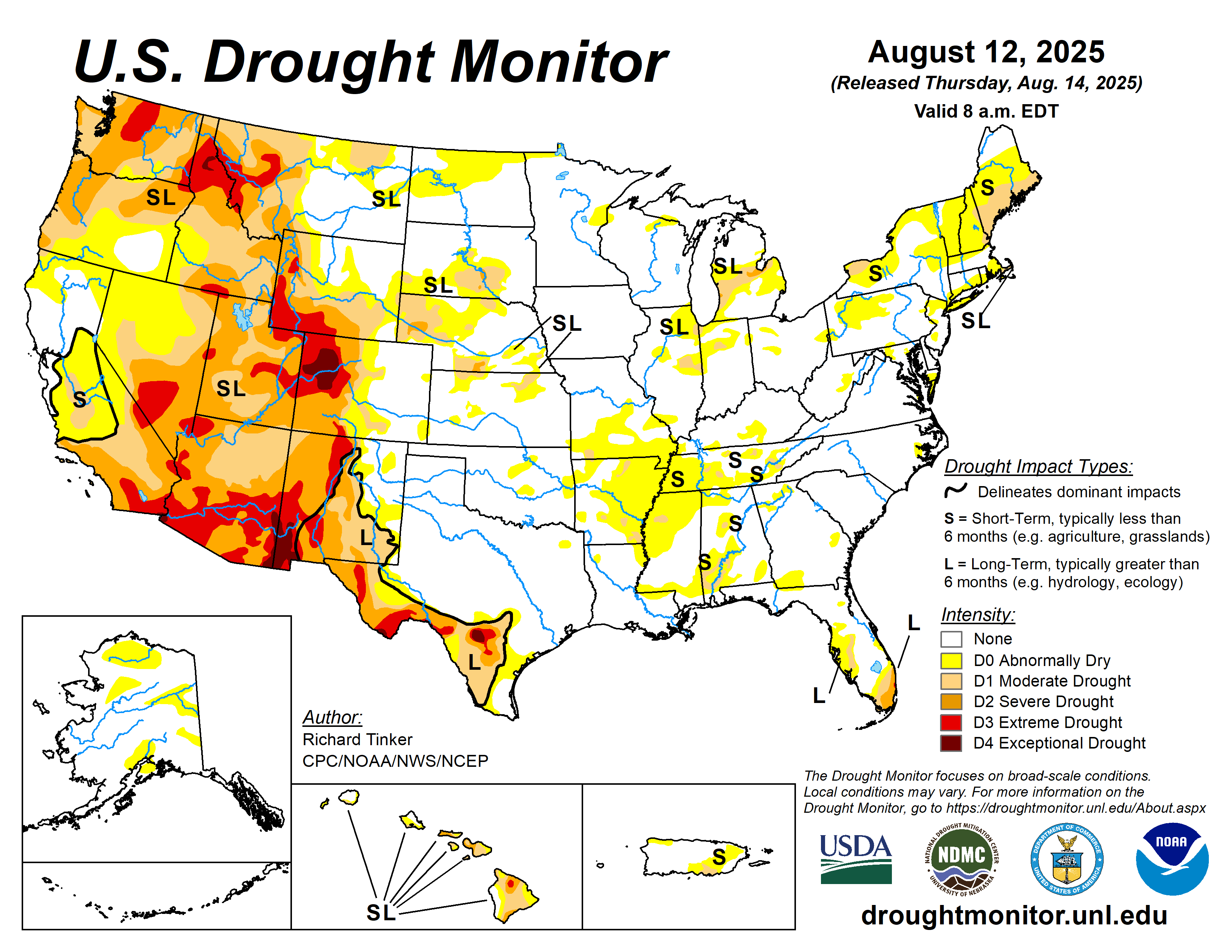
Midwest U.S. Drought Monitor
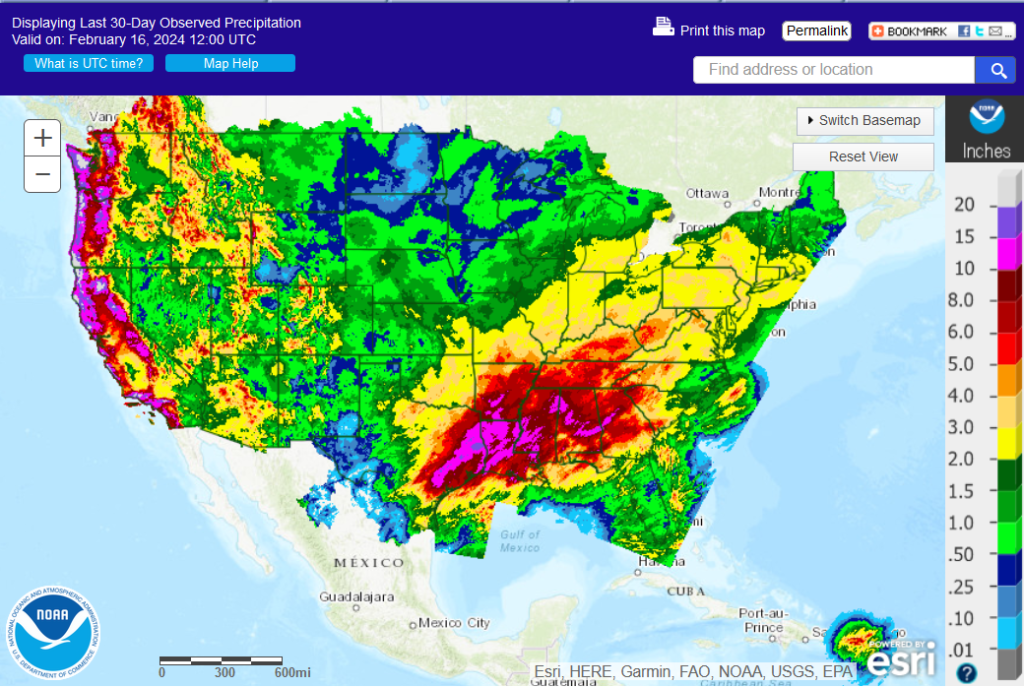
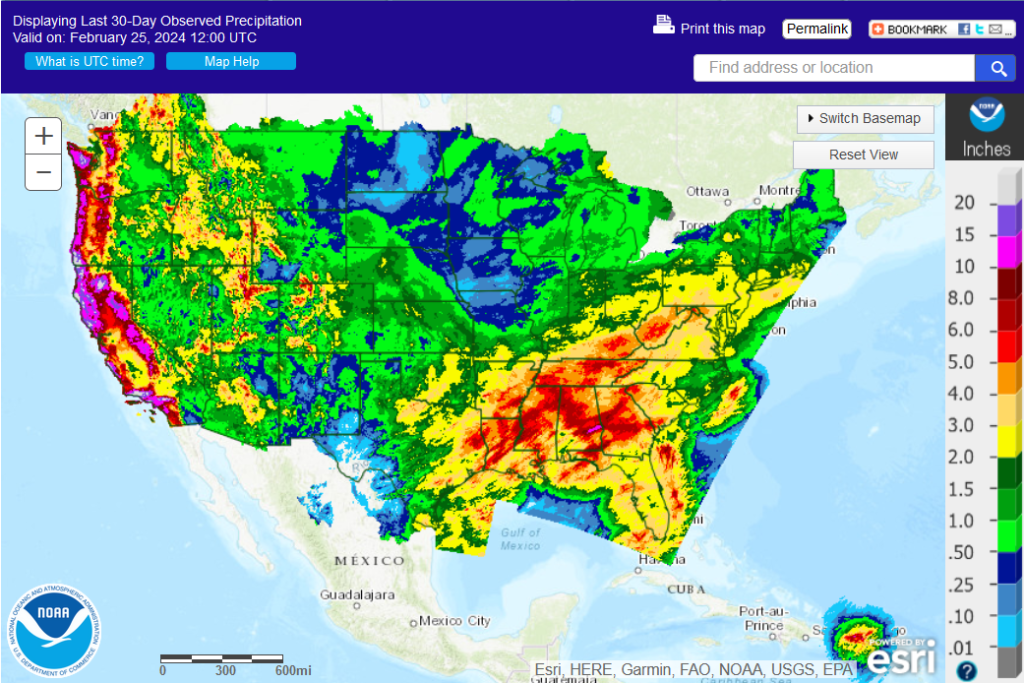
30 Day Precipitation:
.
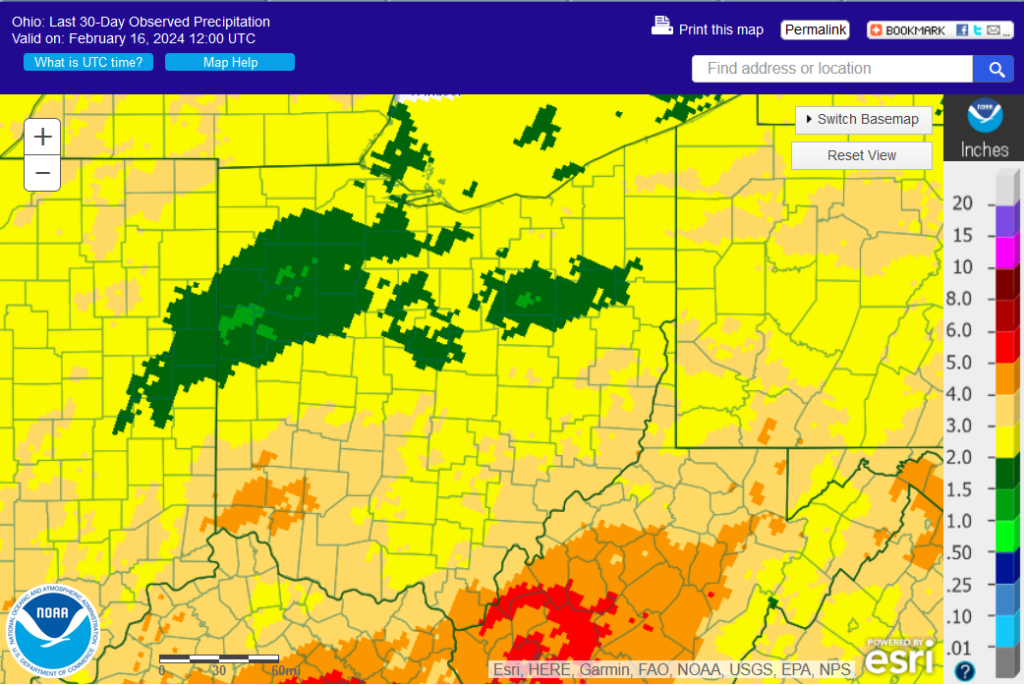
Ohio 30-Day Precipitation
.
Weekly Weather and Crop Bulletin>>>
.
Snow Cover U.S. and Northern Hemisphere >>>
.
.
.
Crop Condition and Soil Moisture Analytics Map:

. .
Search condition monitoring reports for the entire US>>>
Click on the title or the graphic (above) to access the
U.S. Weekly Drought MonitorPDF Version of Graphic
Click on the title or the graphic (above) to access the
U.S. Monthly Drought OutlookPDF Version of Graphic
Click on the title or the graphic (above) to access the
U.S. Seasonal Drought Outlook. PDF Version of Graphic
Other Drought links:
- NWS Drought Fact Sheet
- North American Drought Monitor (NADM)
- National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS)
- National Drought Mitigation Center (NDMC)
- National drought summary>>>
Please remember to water…correctly!
Water once per week, one inch per week, under the entire branch spread, in the absence of rain, May through November. Either rainfall or your watering should equal the one inch per week. Do not water if the soil is already moist. Put out a sprinkler and a straight sided soup can or rain gauge and measure one inch per week. Measure the rainfall which falls in your yard. Your trees don’t care what fell at the airport!
If burlap was left on new trees, it will repel water and the tree or shrub may die. Be sure burlap and twine are removed from the top of all root balls. If your landscaper disagrees, refer him or her to the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) industry standard for installation of landscape plants.
To the extent possible recycle fallen leaves back into the soil around the trees and maintain mulch around the trees to a radius of at least 3-5 feet. Keep mulch off trunks. Use a coarse textured mulch. Avoid triple shredded mulch. Aged arborist wood chips ( https://getchipdrop.com/ ), mulched and composted leaves, pine bark, and pine straw are all good. Very finely ground mulches such as triple ground hardwood mulch are not beneficial and may inhibit moisture and oxygen exchange.
Drought: How Dry Seasons Affect Woody Plants >>>
1-inch capacity rain gauge >>>
Taylor rain gauge >>>
Watering: How and when>>>
Watering Trees and Shrubs>>>

Metal Rectangular Spot Sprinkler
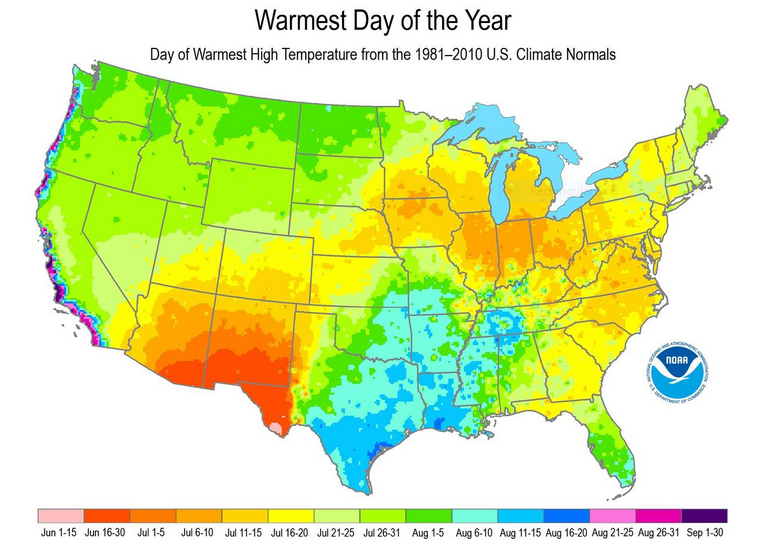
Meteorological Versus Astronomical Seasons
You may have noticed that Arbor Doctor, meteorologists and climatologists define seasons differently from “regular” or astronomical spring, summer, fall, and winter. So, why do meteorological and astronomical seasons begin and end at different times? Climatologically, the period July 14-21, the mid-point of meteorological summer, is the hottest week of the year and the period January 14-21, the mid-point of meteorological winter, is the coldest week of the year over much of the continental US including the Ohio valley.
–
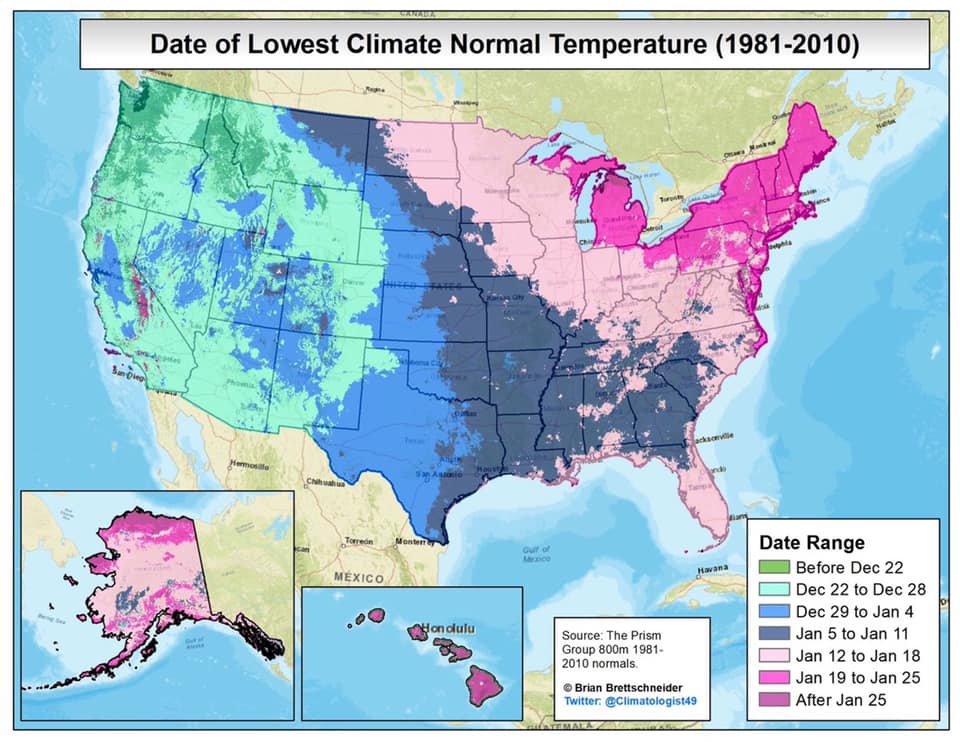
Nearly half the country has had its coldest day by the first day of calendar winter. That is why meteorological winter makes the most sense.
–
Soil temperature map
Soil temperatures across the US.
http://greencastonline.com/tools/SoilTempMaps.aspx>>>
–