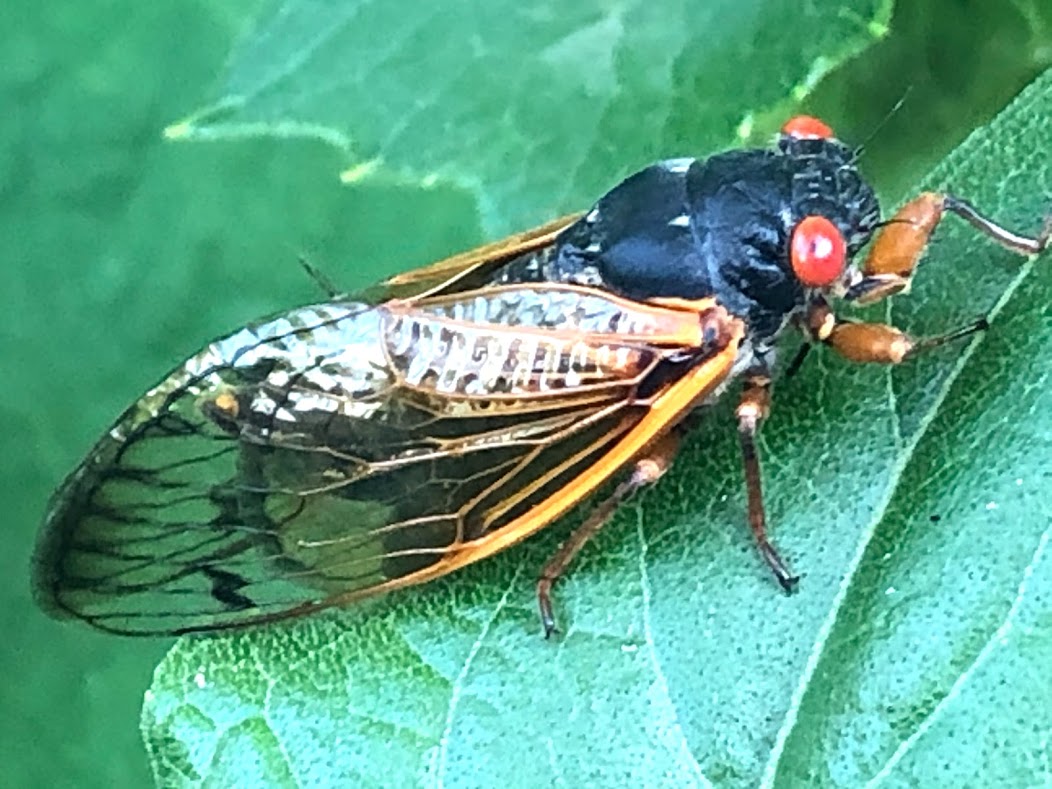
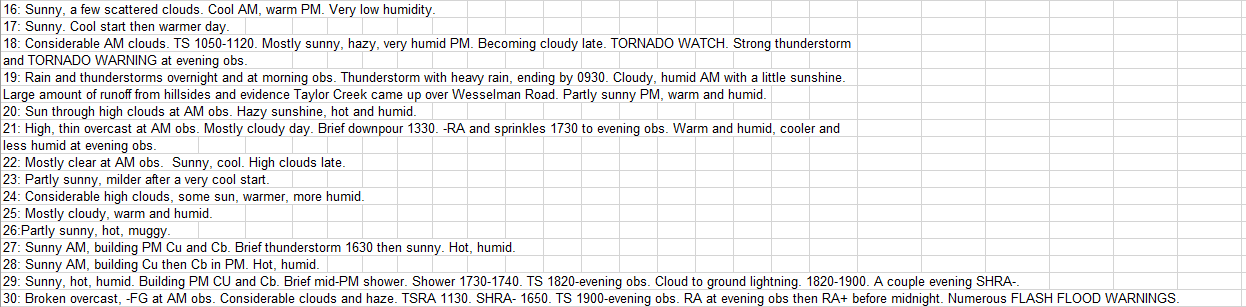
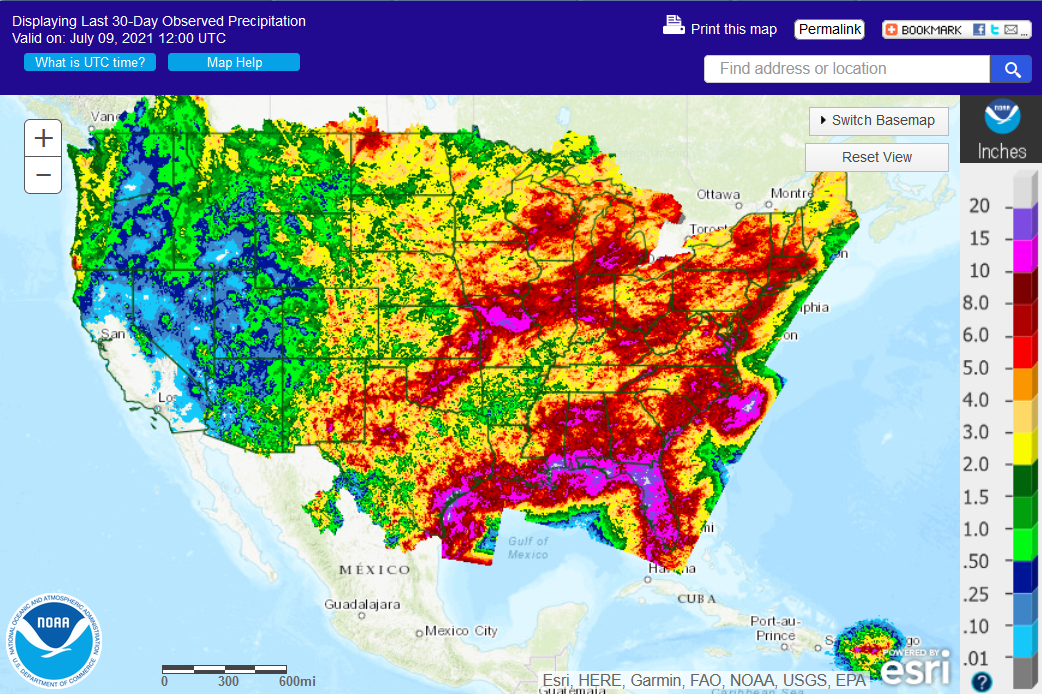
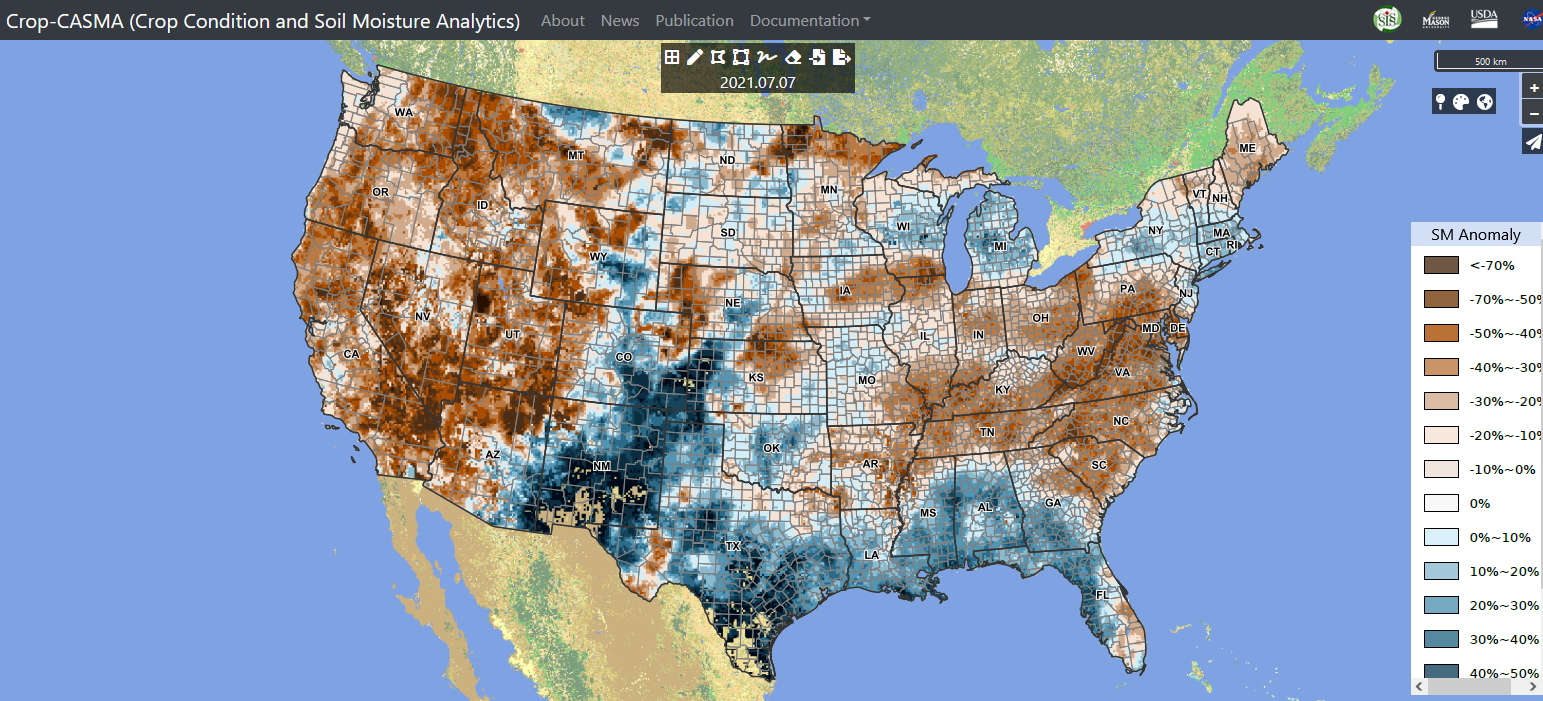
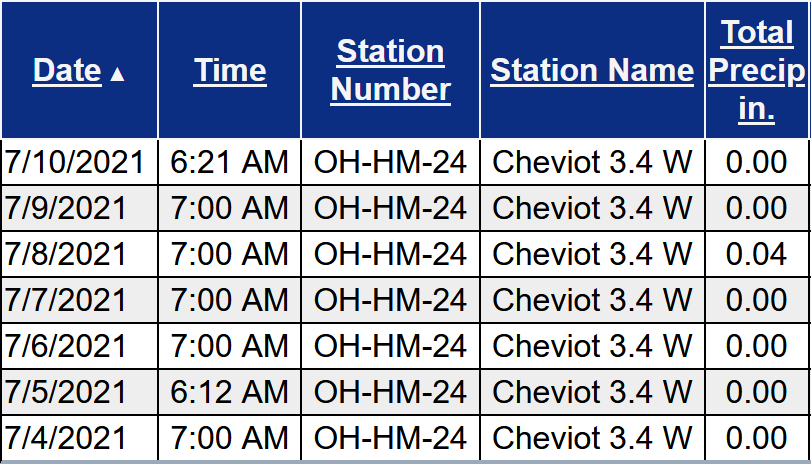
Brood X Cicadas dominated the headlines in June 2021, although flooding rains washed away some of the cicada news during the third week of the month.
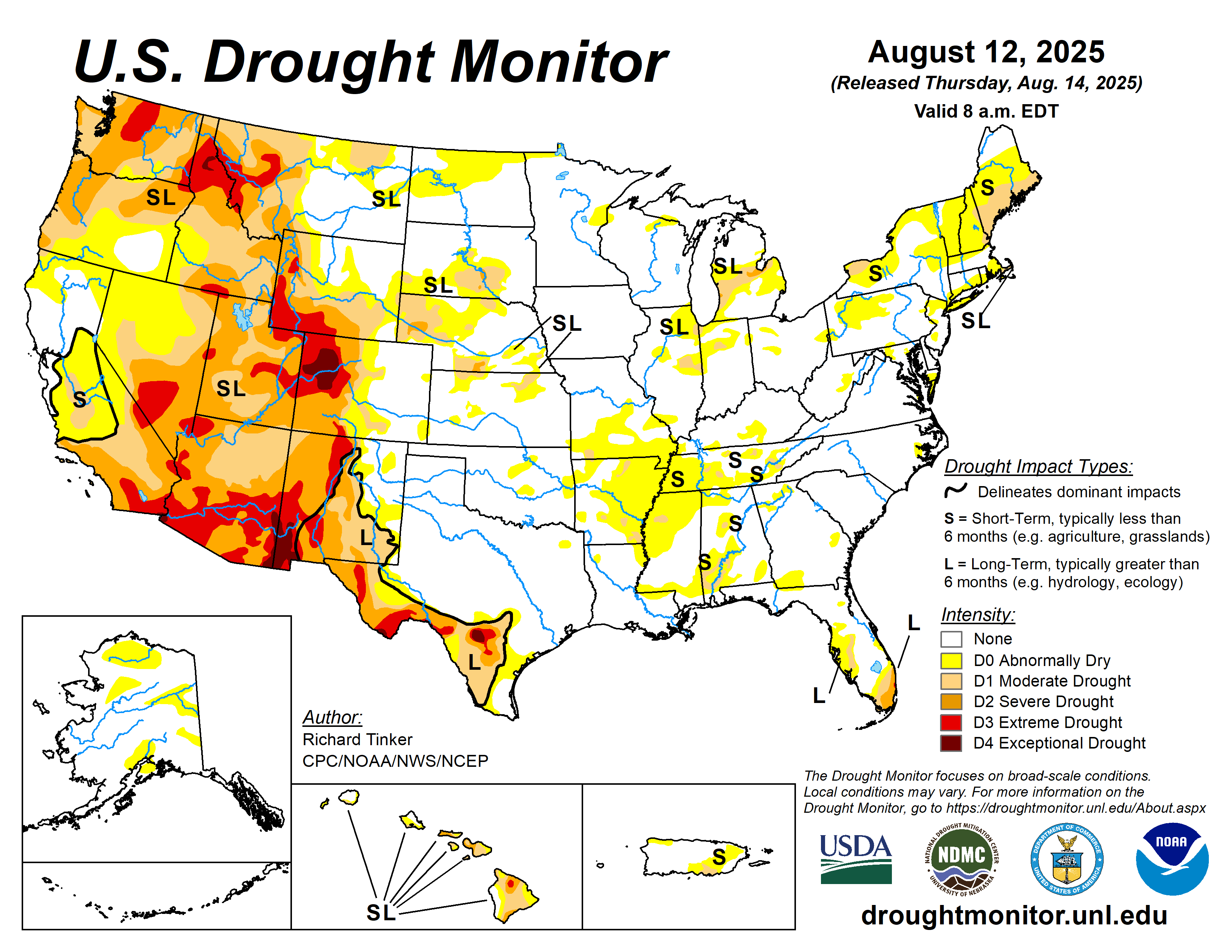
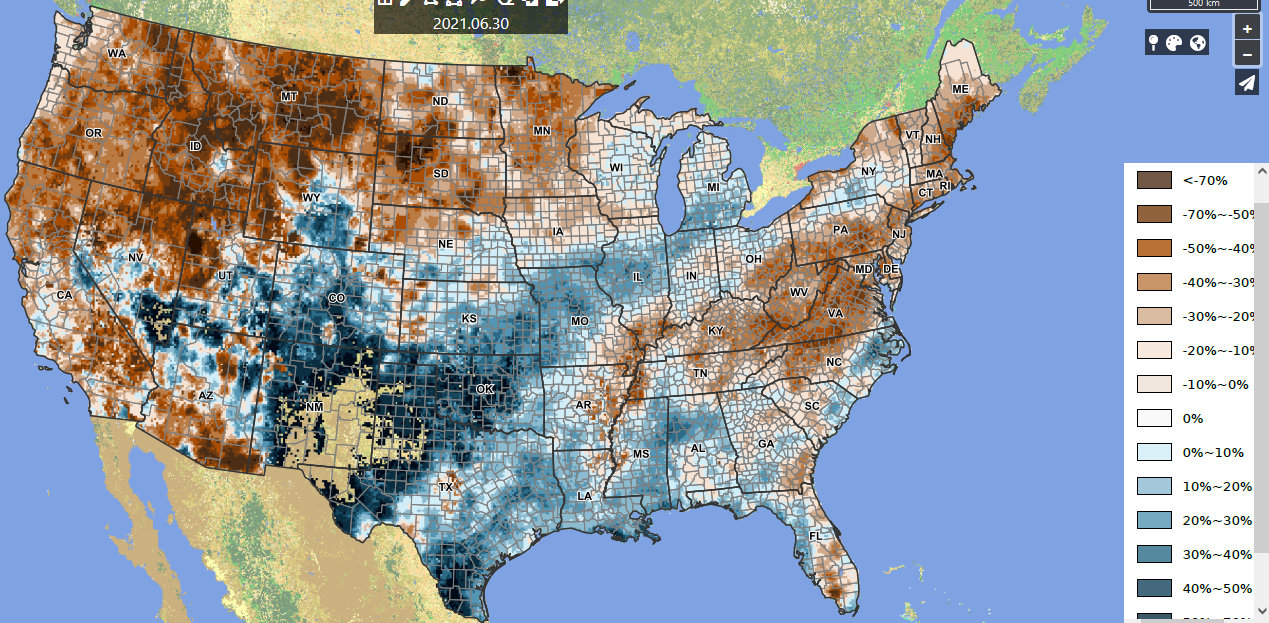
Regional Climate Report – June 2021>>>
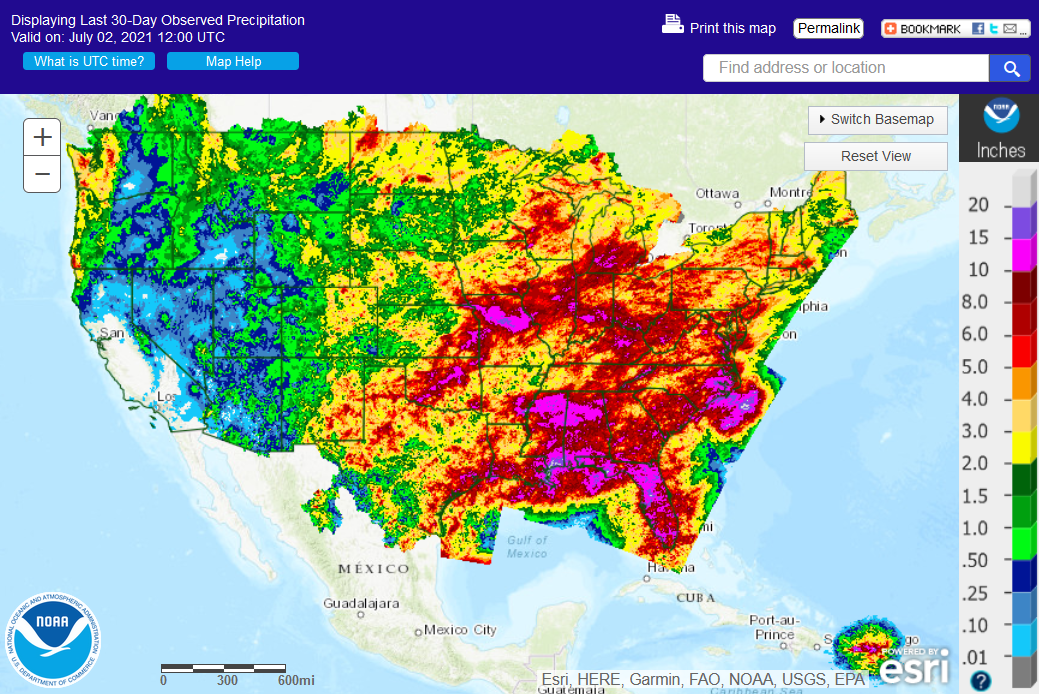
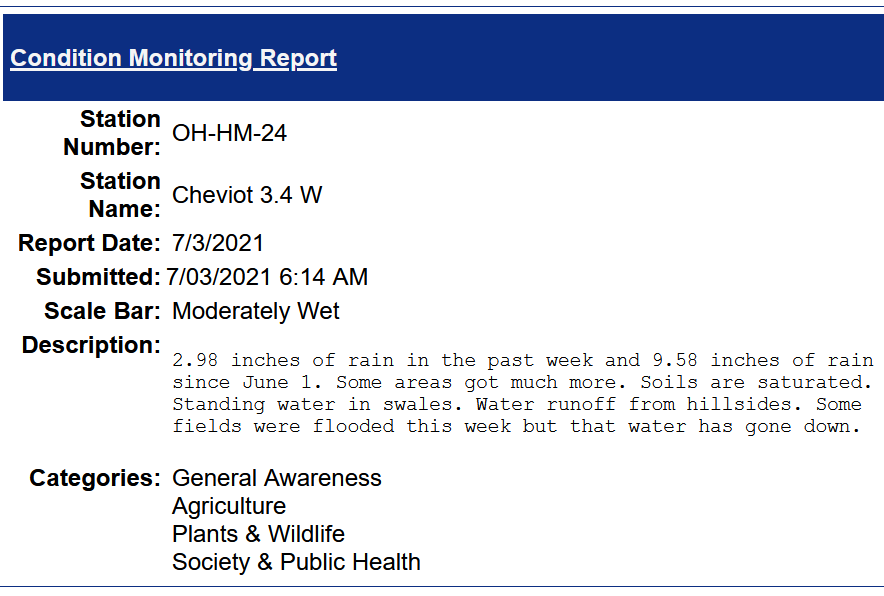
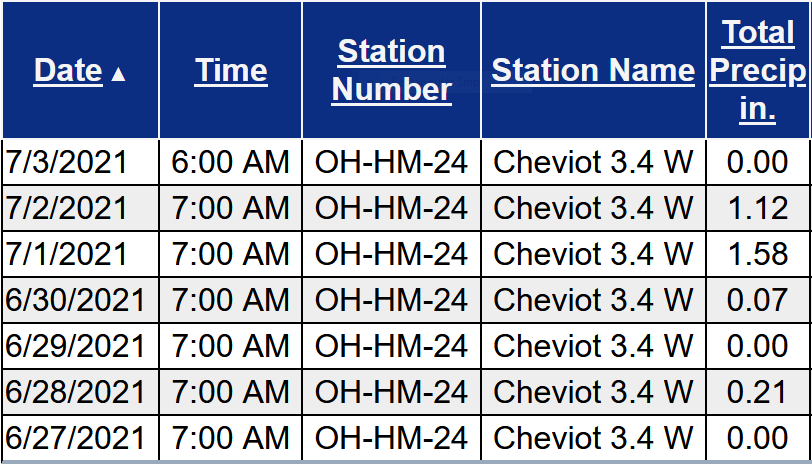
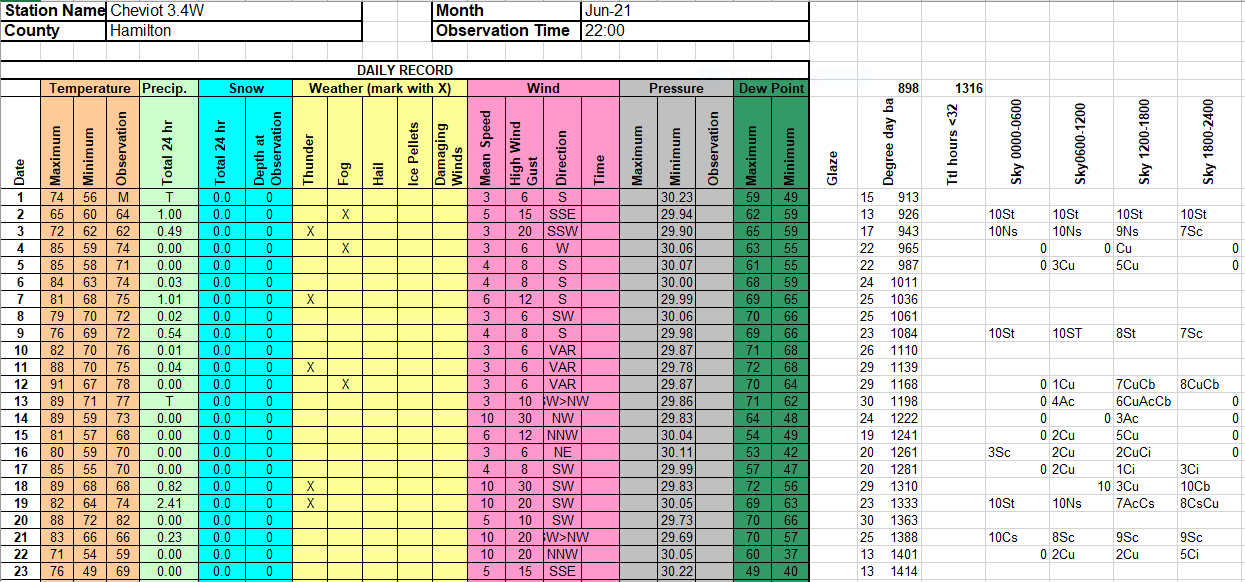
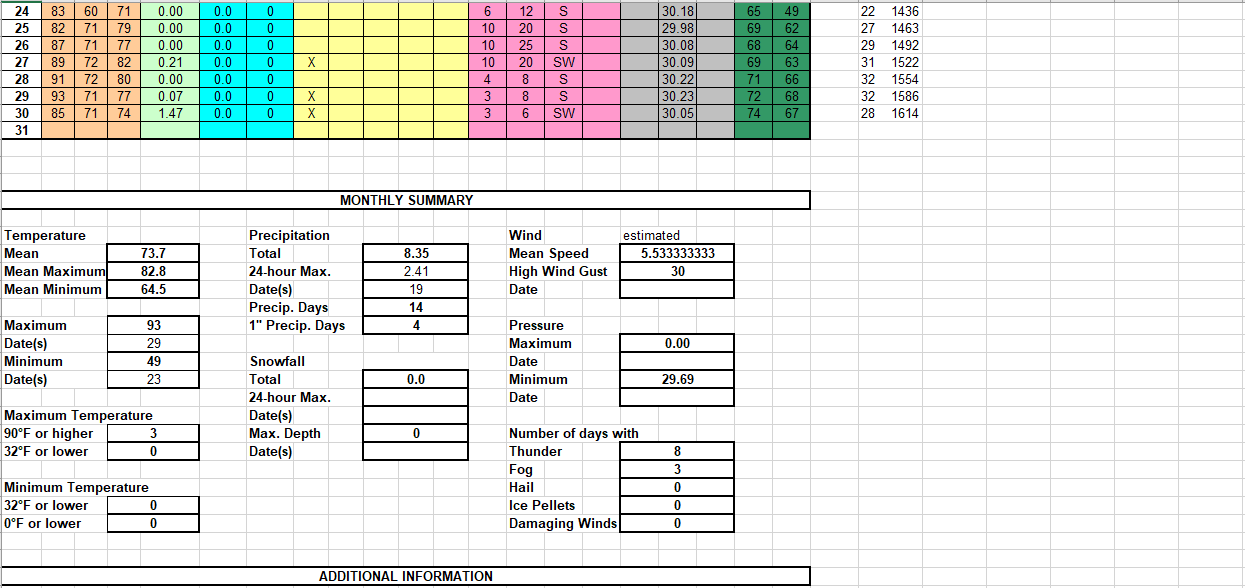
June 18-19, 2021 — Severe Weather and Flash Flooding>>>
June 11, 2021 — Tornado in Lewis County KY>>>
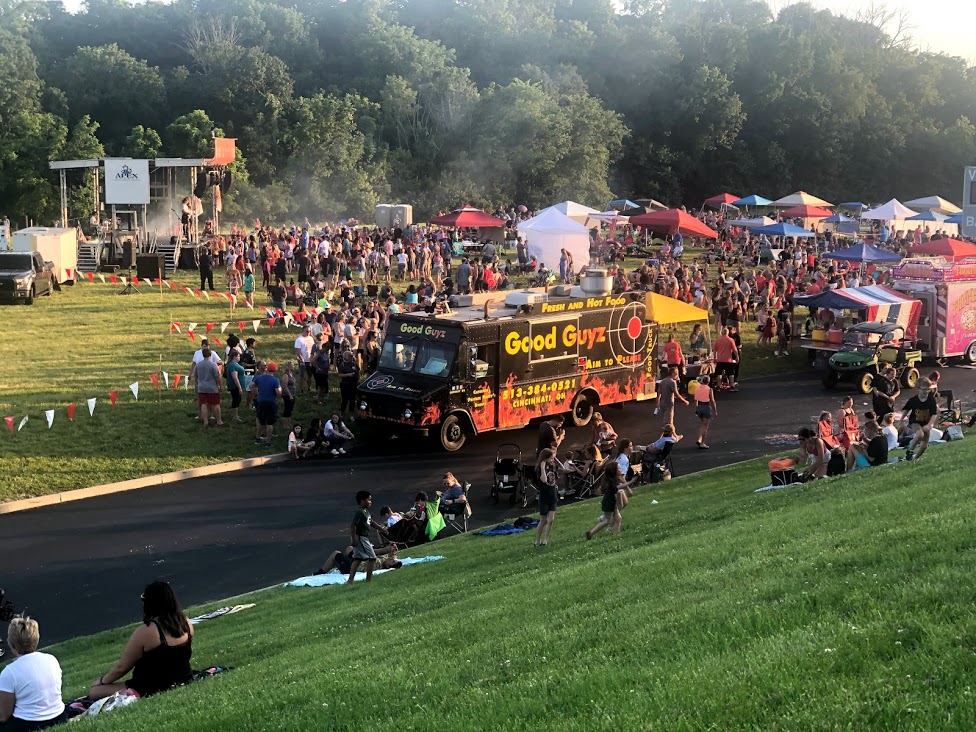

Crossroads West church hosted a festival and fireworks on the last Saturday in June, signaling a return to some normalcy after the long COVID winter.

June bloom of the bottlebrush buckeye.

June bloom of the common milkweed and butterfly weed.



 >>>
>>>